3d Printing In Education
Technological Advancements in Education
One of the areas undeniably impacted by advancing technology is education. Technological developments have made learning processes more innovative. With the integration of these innovative approaches into educational practices, technological opportunities that were previously inaccessible in traditional classroom settings have become available, making learning processes more effective. These advancements have expanded the boundaries of education by providing teachers and students with greater access to resources.
Recently, some technologies that have become more accessible and have made a significant impact on education include digital learning platforms, virtual reality technologies, artificial intelligence, personalized learning, and, of course, 3D printing technologies.
Let’s explore 3D printing technology and its role in education together.
Definition of 3D Printing
3D printing is one of the rapidly developing and widely adopted technologies, frequently used in various fields, including education, alongside its primary applications in manufacturing. This additive manufacturing method involves the physical production of objects designed in computer-based design programs by adding material layer by layer through 3D printers.

In addition to being easily accessible and cost-effective, its ability to be implemented in almost any environment makes it even more appealing.
However, as we will discuss below, despite its advantages, the application of 3D printing may face certain challenges in underdeveloped and developing countries.
Applications of 3D Printing Technology in Education
The use of this technology in education can be evaluated in three stages:
3D Printing in Preschool and Primary Education
This period is a critical threshold for children in terms of cognitive development. During this stage, children learn the differences between concrete and abstract concepts. Due to their cognitive processes, their ability to comprehend abstract concepts is limited, and they require tangible examples to develop this skill.
With 3D printing technologies, physical objects that can be directly observed and contribute to the cognitive development of students at this age can be produced. In addition to keeping their interest in school, education, and digital technologies alive, these technologies help foster their cognitive growth. Furthermore, exploring these technologies closely can contribute to shaping their life vision at an early stage, shedding light on their future.
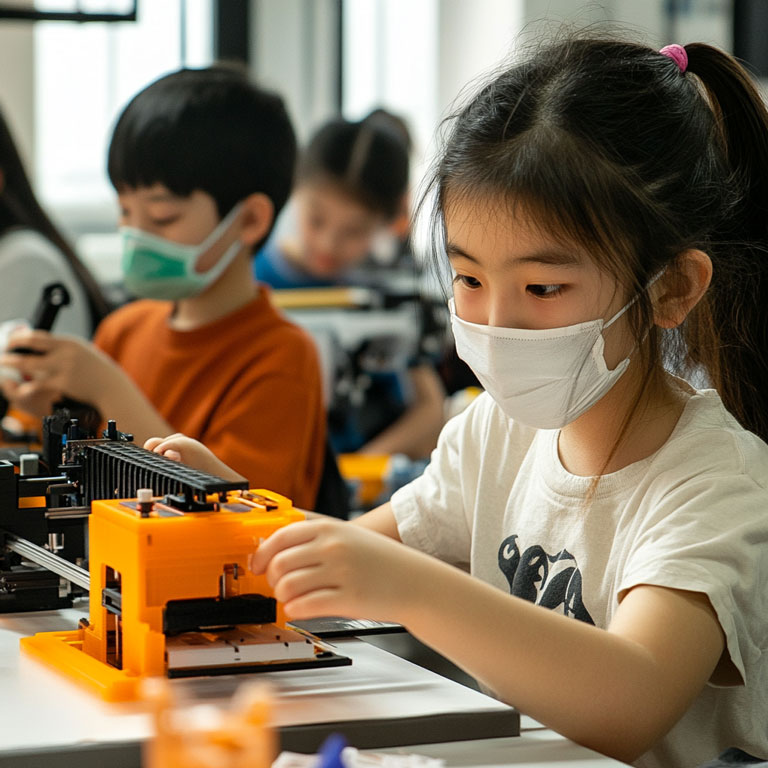

3D Printing Applications in Secondary Education
In secondary education, 3D printing is frequently used to model concepts discussed in classes and to bring to life designs for project-based lessons using 3D printers. For students, creating real-world models of their designs provides motivation for tackling more complex projects.
As these students transition to higher education, the vision and familiarity they gain through these experiences encourage them to achieve even greater accomplishments.
3D Printing in Higher Education and Vocational Training
In this stage, a critical skill for students as they prepare for the professional working world is the ability to translate theoretical knowledge into practice. Learning prototype development and production techniques, particularly in engineering and design courses, is among the opportunities that 3D printing technology offers to students.
In today’s world, adapting to constantly changing trends and an evolving technological environment is a crucial skill for students. For this reason, higher education and vocational training students should enhance their creative and innovative thinking abilities through participation in group projects and project management processes. 3D printing technologies stand out as one of the primary tools that can support them in these processes.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Education
- Materialization of abstract concepts
- Enabling students to learn through hands-on experience
- Rapid prototyping
- Providing alternatives to traditional educational materials
- Promoting group collaboration environments
- Offering opportunities for project-based learning
Skills Developed by 3D Printing in Education
- 3D Modeling
- Visualization
- Teamwork and communication
- Design and creativity
- Problem-solving skills
- Innovative thinking skills
Research on 3D Printing and Education
The scientific study titled “Opportunities and Challenges in Integrating 3D Printing into Engineering Education in Developing Countries”, published in the journal Educational Technology & Society, discusses the challenges encountered during the integration of this technology into higher education and suggests some measures to overcome them. The research was conducted as a survey study with contributions from higher education institutions in Vietnam.
The study was designed to analyze the perspectives of higher education students and faculty members in Vietnam who are engaged in 3D printing education. A total of 307 participants, including 272 students and 35 faculty members from 12 universities in Vietnam, took part in the study. It is noted that the data collected from the participants were evaluated using both quantitative and qualitative analysis methods. Participation in the survey was voluntary, and the survey questions aimed to assess participants’ views on the applications of 3D printing in education, the challenges they faced, and the benefits of the technology.
Other factors focused on in the study include:
- Curriculum alignment
- Faculty training
- Costs
- Language barriers
- Technical proficiency
Let’s explore the findings of the study together.
Barriers Faced by Students and Academics in Integrating 3DP into the Classroom
This section focuses on some of the responses from the survey to examine the barriers that students and academics believe they face in integrating 3D printing into the classroom.
The primary barriers faced by students in integrating 3D printing into the classroom include insufficient technology, high equipment costs, and material limitations. Other obstacles reported by students include technological limitations, limited application opportunities, lack of motivation, insufficient English proficiency, and inadequate resources for participation.
Academics, on the other hand, indicated that they encounter certain challenges in teaching processes. These challenges include difficulties related to inappropriate curriculum design, insufficient educational resources, and issues with purchasing materials and equipment.
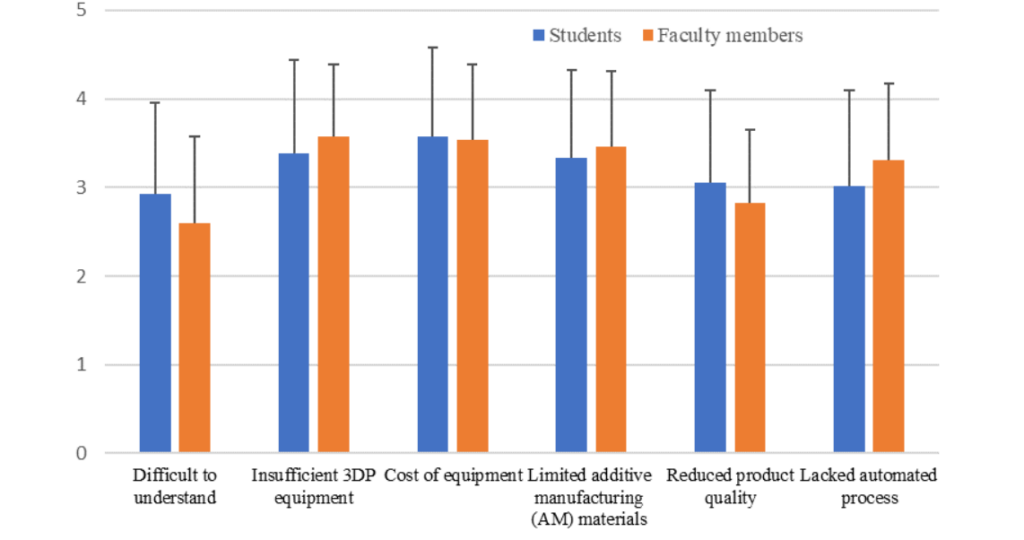
One of the survey questions, “How would you evaluate the barriers to integrating 3DP in the classroom?” clearly highlights these barriers. Both academics and students rated their responses on a 5-point scale. As shown in the graph below, the top three barriers are identified as “Insufficient Equipment,” “Equipment Cost,” and “Material Limitations.”
The most significant differences in perceived barriers between students and academics were observed in the factors “Difficult to Understand” and “Lacked Automated Process.”
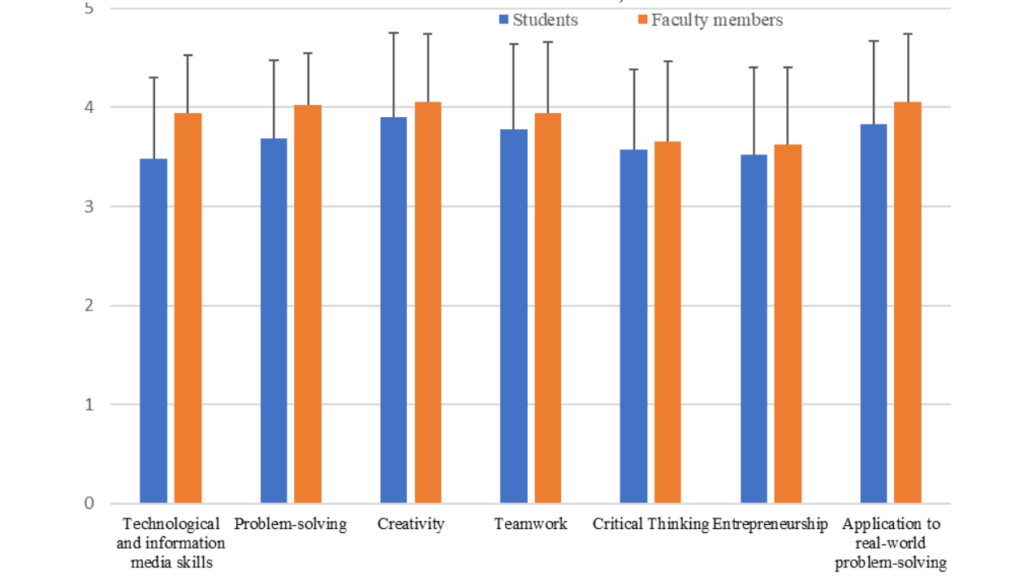
Another question I would like to address is: “Will 3DP help students achieve 21st-century skills?” This question, posed to both students and academics, aims to understand and analyze the contributions of 3D printing technology to students’ next-generation skills.
Both groups indicated that 3DP significantly contributes to the development of skills such as creative thinking, problem-solving, collaboration, and effective use of technology. However, differences were observed in certain aspects between academics and students. One notable difference is that academics appear to believe more strongly than students in 3DP’s potential to enhance critical thinking skills.
References
To, T. T., Al Mahmud, A., & Ranscombe, C. (2024). Opportunities and challenges of 3D printing integration into engineering education in developing countries. Educational Technology & Society, 27(4), 191-217. https://doi.org/10.30191/ETS.202410_27(4).RP11